Remove cycles and bidirected edges from a directed graph.
Usage
graph2dag(graph, data, bap = FALSE, time.limit = Inf, ...)
Arguments
- graph
A directed graph as an igraph object.
- data
A data matrix with subjects as rows and variables as
columns.
- bap
If TRUE, a bow-free acyclic path (BAP) is returned
(default = FALSE).
- time.limit
CPU time for the computation, in seconds
(default = Inf).
- ...
Currently ignored.
Value
A DAG as an igraph object.
Details
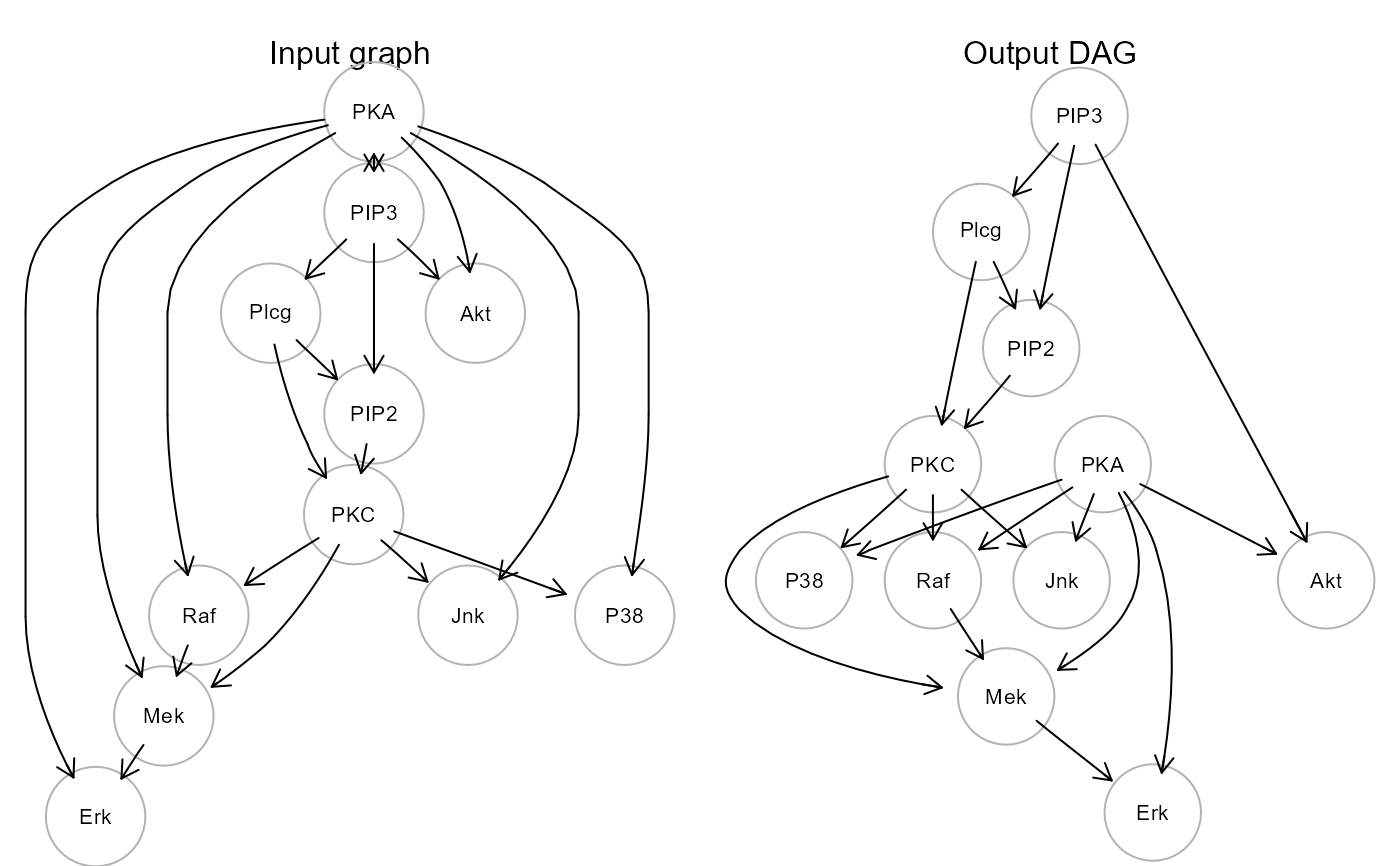
The conversion is performed firstly by removing bidirected
edges and then the data matrix is used to compute edge P-values, through
marginal correlation testing (see weightGraph,
r-to-z method). When a cycle is detected, the edge with highest
P-value is removed, breaking the cycle. If the bap argument is TRUE,
a BAP is generated merging the output DAG and the bidirected edges
from the input graph.
Examples
dag <- graph2dag(graph = sachs$graph, data = log(sachs$pkc))
#> DAG conversion : TRUE
old.par <- par(no.readonly = TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1,2), mar=rep(1, 4))
gplot(sachs$graph, main = "Input graph")
gplot(dag, main = "Output DAG")
 par(old.par)
par(old.par)
