This function uses SEMace to find
significant causal effects between source-sink pairs and
SEMpath to fit them and test their edge
perturbation.
Usage
pathFinder(
graph,
data,
group = NULL,
ace = NULL,
path = "directed",
method = "BH",
alpha = 0.05,
...
)Arguments
- graph
Input network as an igraph object.
- data
A matrix or data.frame. Rows correspond to subjects, and columns to graph nodes (variables).
- group
group A binary vector. This vector must be as long as the number of subjects. Each vector element must be 1 for cases and 0 for control subjects. Group specification enables edge perturbation testing. By default,
group = NULL.- ace
A data.frame generated by
SEMace. If NULL,SEMacewill be automatically run.- path
If
path = "directed", all directed paths between the two nodes will be included in the fitted model. Ifpath = "shortest", only shortest paths will be considered.- method
Multiple testing correction method. One of the values available in
p.adjust. By default,method = "BH"(i.e., FDR multiple test correction).- alpha
Significance level for ACE selection (by default,
alpha = 0.05).- ...
Currently ignored.
Value
A list of 3 objects:
"paths", list of paths as igraph objects;
"fit", fitting results for each path as a lavaan object;
"dfp", a data.frame containing SEM global fitting statistics.
Author
Fernando Palluzzi fernando.palluzzi@gmail.com
Examples
# \donttest{
# Find and evaluate significantly perturbed paths
# Nonparanormal(npn) transformation
als.npn <- transformData(alsData$exprs)$data
#> Conducting the nonparanormal transformation via shrunkun ECDF...done.
adjData <- SEMbap(alsData$graph, als.npn)$data
#> Bow-free covariances search. Use method: cggm ...
#> Number of bow-free covariances / df : 220 / 420
#> Max parent set(S) / Sparsity idx(s) : 10 / 4
#> Number of clusters / number of nodes: 2 / 31
#>
paths <- pathFinder(alsData$graph, adjData,
group = alsData$group,
ace = NULL)
#>
#> Frequency distribution of path length from X to Y :
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> 45 21 16 12 6
#>
#>
ACE= 1 of 100
ACE= 2 of 100
ACE= 3 of 100
ACE= 4 of 100
ACE= 5 of 100
ACE= 6 of 100
ACE= 7 of 100
ACE= 8 of 100
ACE= 9 of 100
ACE= 10 of 100
ACE= 11 of 100
ACE= 12 of 100
ACE= 13 of 100
ACE= 14 of 100
ACE= 15 of 100
ACE= 16 of 100
ACE= 17 of 100
ACE= 18 of 100
ACE= 19 of 100
ACE= 20 of 100
ACE= 21 of 100
ACE= 22 of 100
ACE= 23 of 100
ACE= 24 of 100
ACE= 25 of 100
ACE= 26 of 100
ACE= 27 of 100
ACE= 28 of 100
ACE= 29 of 100
ACE= 30 of 100
ACE= 31 of 100
ACE= 32 of 100
ACE= 33 of 100
ACE= 34 of 100
ACE= 35 of 100
ACE= 36 of 100
ACE= 37 of 100
ACE= 38 of 100
ACE= 39 of 100
ACE= 40 of 100
ACE= 41 of 100
ACE= 42 of 100
ACE= 43 of 100
ACE= 44 of 100
ACE= 45 of 100
ACE= 46 of 100
ACE= 47 of 100
ACE= 48 of 100
ACE= 49 of 100
ACE= 50 of 100
ACE= 51 of 100
ACE= 52 of 100
ACE= 53 of 100
ACE= 54 of 100
ACE= 55 of 100
ACE= 56 of 100
ACE= 57 of 100
ACE= 58 of 100
ACE= 59 of 100
ACE= 60 of 100
ACE= 61 of 100
ACE= 62 of 100
ACE= 63 of 100
ACE= 64 of 100
ACE= 65 of 100
ACE= 66 of 100
ACE= 67 of 100
ACE= 68 of 100
ACE= 69 of 100
ACE= 70 of 100
ACE= 71 of 100
ACE= 72 of 100
ACE= 73 of 100
ACE= 74 of 100
ACE= 75 of 100
ACE= 76 of 100
ACE= 77 of 100
ACE= 78 of 100
ACE= 79 of 100
ACE= 80 of 100
ACE= 81 of 100
ACE= 82 of 100
ACE= 83 of 100
ACE= 84 of 100
ACE= 85 of 100
ACE= 86 of 100
ACE= 87 of 100
ACE= 88 of 100
ACE= 89 of 100
ACE= 90 of 100
ACE= 91 of 100
ACE= 92 of 100
ACE= 93 of 100
ACE= 94 of 100
ACE= 95 of 100
ACE= 96 of 100
ACE= 97 of 100
ACE= 98 of 100
ACE= 99 of 100
ACE= 100 of 100
#>
ACE= 1 of 3
ACE= 2 of 3
ACE= 3 of 3
#> Found 2 significant ACEs with > 2 nodes
#>
print(paths$dfp)
#> pathId sink op source n.nodes n.edges dev_df srmr V.pv.act V.pv.inh
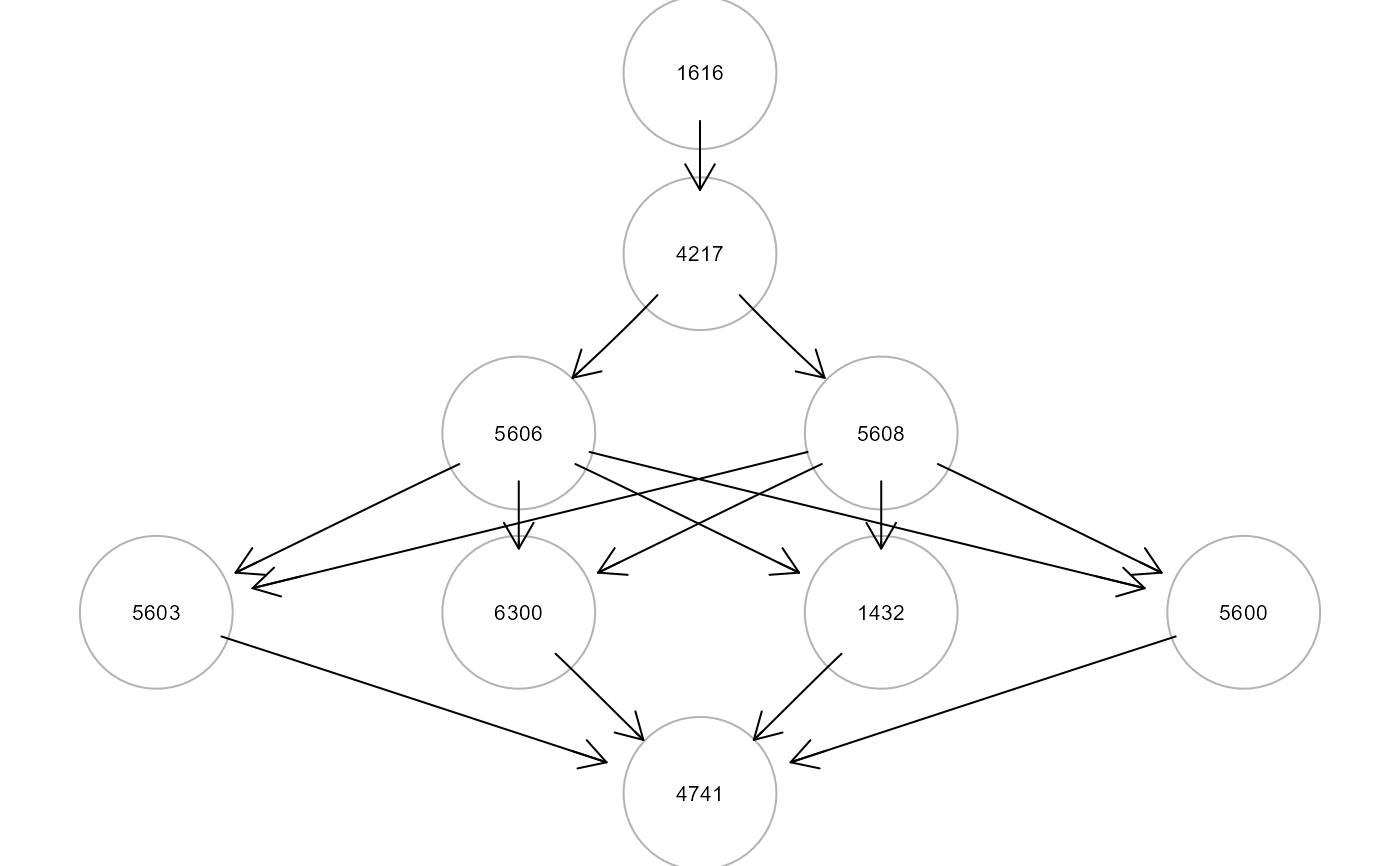
#> 1 P16168 4741 <- 1616 9 15 2.250 0.065 0.000000 0.035968
#> 2 P5962 842 <- 596 3 2 0.369 0.015 0.242861 0.611600
head(parameterEstimates(paths$fit[[1]]))
#> lhs op rhs est se z pvalue ci.lower ci.upper
#> 1 1432 ~ group -0.017 0.072 -0.240 0.810 -0.157 0.123
#> 2 1616 ~ group 0.105 0.079 1.329 0.184 -0.050 0.259
#> 3 4217 ~ group 0.062 0.077 0.800 0.424 -0.089 0.212
#> 4 4741 ~ group 0.444 0.073 6.108 0.000 0.302 0.587
#> 5 5600 ~ group -0.296 0.076 -3.911 0.000 -0.445 -0.148
#> 6 5603 ~ group 0.003 0.079 0.032 0.975 -0.153 0.158
gplot(paths$paths[[1]])
 # }
# }